NEWS
Hochrangige Fachpublikation zur Verbesserung der KI-gestützten Blutflusssimulation
Ein Forschungsteam der Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Siemens Healthineers und der STIMULATE-Forschungsgruppe Medical Flows der Otto-von-Guericke-Universität Magdeburg (OVGU) haben wichtige Forschungsergebnisse im hochrangigen Fachjournal Computers in Biology and Medicine (Impact Factor 7) veröffentlicht. Die Studie befasst sich mit der Weiterentwicklung der sogenannten vierdimensionalen digitalen Subtraktionsangiographie (4D-DSA), einer Bildgebungstechnik zur Visualisierung der Blutgefäße und zur kontrastmittelbasierten Blutflussquantifizierung.
Der Hauptfortschritt besteht darin, dass die herkömmliche 3D-DSA die detaillierte Darstellung der Gefäßanatomie ermöglicht, während die neue 4D-DSA-Technologie zusätzlich den zeitlichen Verlauf des Blutflusses in 3D erfasst. Die Rekonstruktion dieser Daten ist jedoch aufgrund von Gefäßüberlagerungen und Verzerrungen schwierig. Um dieses Problem zu lösen, entwickelten die Forschenden ein neuronales Netzwerk, das auf simulationsbasierten Blutflussbildern trainiert wurde. Das Modell sagt die Kontrastmittelkonzentration entlang der Gefäße präzise vorher und reduziert den Rechenaufwand. Es ist zudem robust gegenüber Überlagerungen und Verzerrungen, was die Genauigkeit der 4D-DSA-Darstellung deutlich verbessert.
Mit der Veröffentlichung der weltweit wichtigen Forschungsergebnisse erreicht das Forschungsteam einen bedeutenden Fortschritt im Bereich der medizinischen Bildgebung. In Zukunft könnten die Ergebnisse dazu beitragen, klinische Diagnosen bei Gefäßerkrankungen zu verbessern.
Die Fachpublikation mit dem Titel „Simulation-informed learning for time-resolved angiographic contrast agent concentration reconstruction“ ist hier einsehbar.
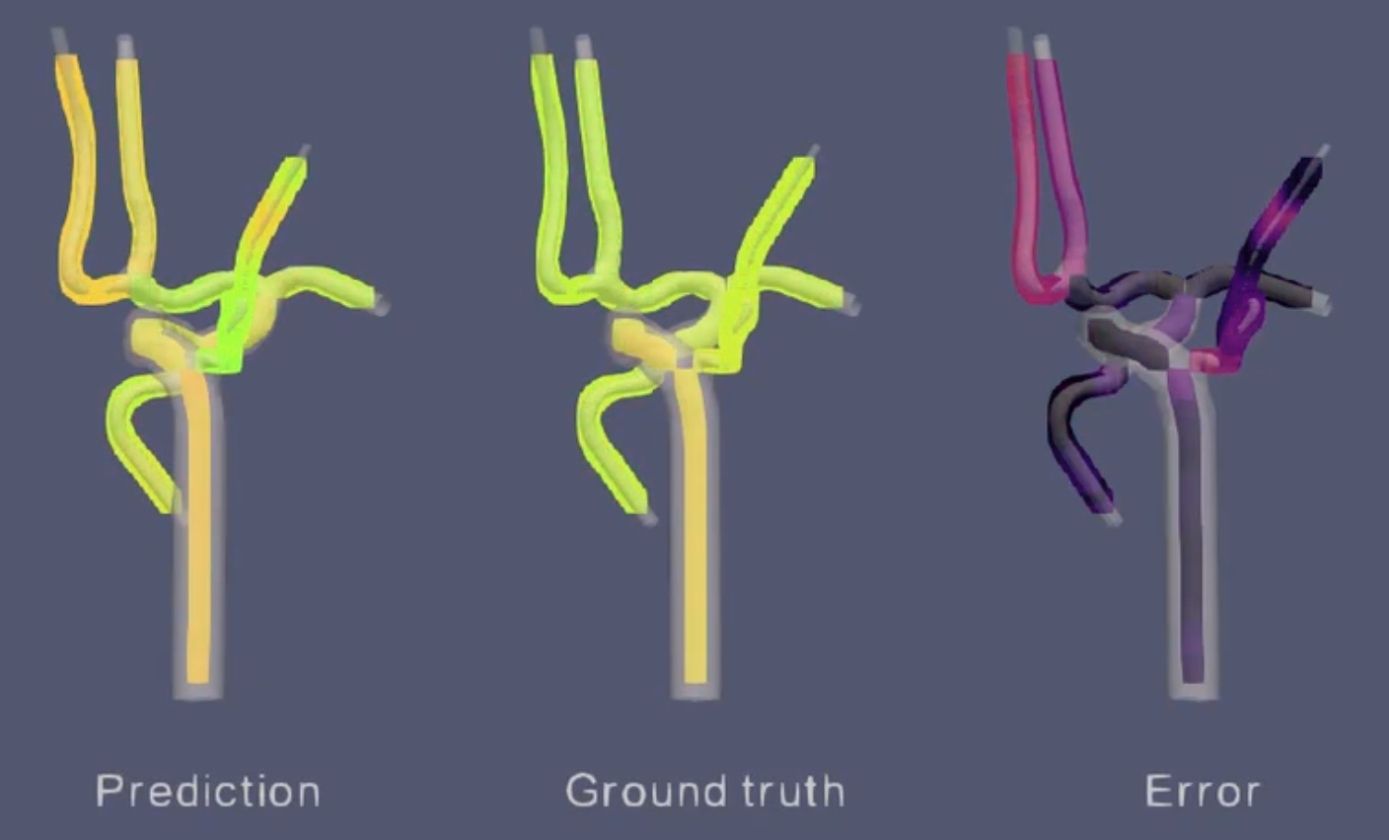
Qualitative Analyse einer Probe des Testsatzes. Darstellung der Kontrastmittelkonzentrationsvorhersage des Netzwerks, der tatsächlichen Konzentration und des absoluten Fehlers. / Qualitative analysis of a sample of the test set. Visualisation of the contrast agent concentration prediction of the network, the actual concentration and the absolute error.
High-ranking scientific publication on the improvement of AI-supported blood flow simulation
A research team from Friedrich-Alexander University Erlangen-Nuremberg, Siemens Healthineers and the STIMULATE Medical Flows research group at Otto-von-Guericke-University Magdeburg (OVGU) have published important research results in the high-ranking journal Computers in Biology and Medicine (Impact Factor 7). The study deals with the further development of so-called four-dimensional digital subtraction angiography (4D-DSA), an imaging technique for the visualisation of blood vessels and contrast agent-based blood flow quantification.
The main advance is that conventional 3D DSA enables the detailed visualisation of vascular anatomy, while the new 4D DSA technology additionally captures the temporal course of blood flow in 3D. However, the reconstruction of this data is difficult due to vascular overlays and distortions. To solve this problem, the researchers developed a neural network that was trained on simulation-based blood flow images. The model precisely predicts the concentration of contrast medium along the vessels and reduces the computational effort. It is also robust against overlays and distortions, which significantly improves the accuracy of the 4D DSA visualisation.
With the publication of the globally important research results, the research team has made significant progress in the field of medical imaging. In future, the results could help to improve clinical diagnoses of vascular diseases.
The specialist publication entitled ‘Simulation-informed learning for time-resolved angiographic contrast agent concentration reconstruction’ can be viewed here.